Factories use giant machines called industrial furnaces. They will heat the materials, to change the material into other forms. These furnaces are essential for the manufacturing processes of products such as metal, glass, and ceramics. We can appreciate their usefulness, even more, when learning about the types of industrial furnaces and how they operate.
Industrial furnaces are large ovens that heat materials to extreme temperatures. The heat softens the materials, making them more malleable. Metal, for instance, can be melted in a furnace. It can be poured into molds and cooled to form various metal parts used in machinery and tools.
Batch Furnaces — used for smaller jobs. You place materials into the furnace, heat them up, and remove then when you're done. For pottery and jewelry making, they are frequently employed.
They have Electric Arc Furnaces: These generate heat using electricity. They melt metals, most notably for recycling, including steel. They are more energy-efficient than gas-powered furnaces.
Industrial furnaces require frequent maintenance to function properly. It entails cleaning them frequently, looking for signs of damage, and replacing broken parts. And the internal temperature and gas levels need to be monitored so that everyone can remain safe.
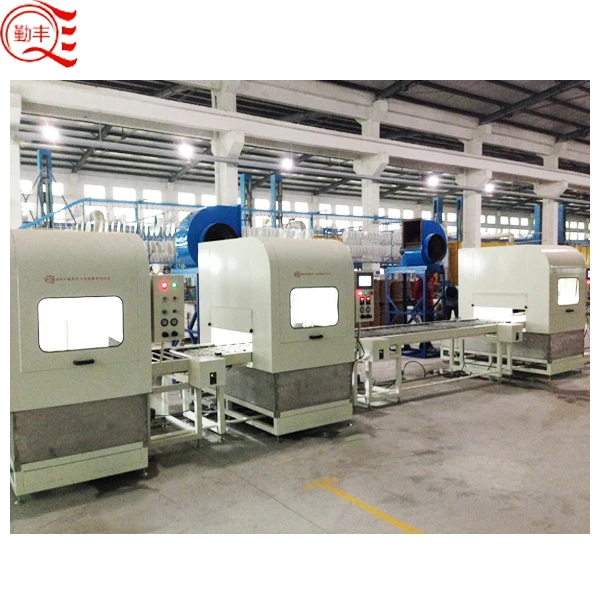

New technology is improving furnaces. New designs use less energy to produce and cause less pollution, so they’re better for the environment. Certain furnaces include sensors and automation to allow for more efficient heating of materials, minimizing waste.
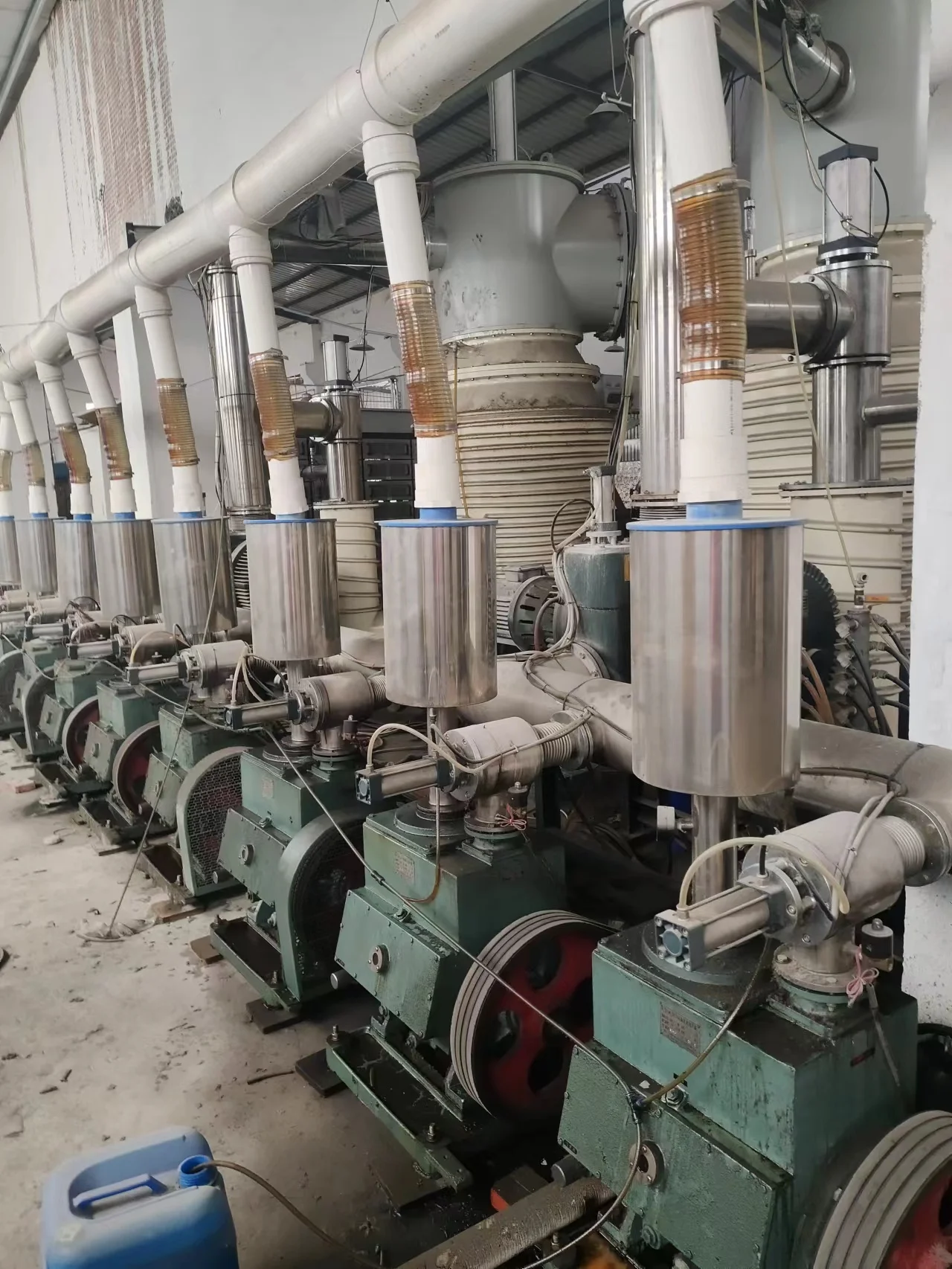

Industrial furnaces where you can do more damage if you do not follow safety rules. To minimize injury from heat and flying debris, workers should wear gloves and goggles. They should also know how to operate the furnace safely, and what to do in an emergency, such as a fire or a leak. There are regulations to protect workers, such as requirements for regular inspections and adhering to pollution rules.
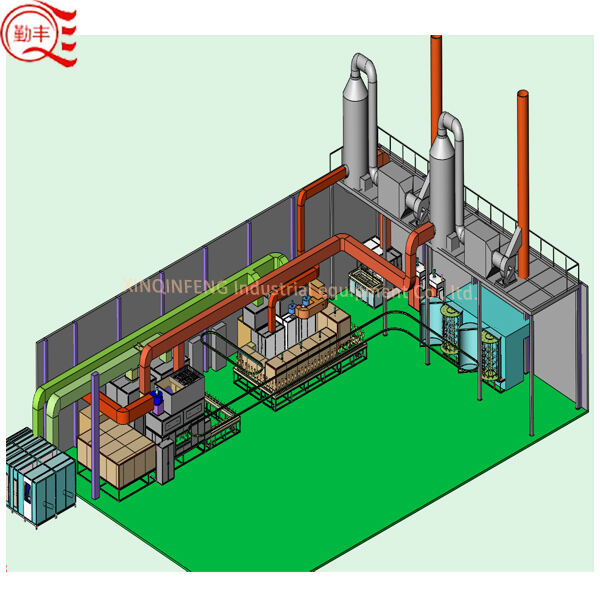
Xinqinfeng make use high-end materials and components for machine. They use first class metal components, imported spraying paint guns from top brands, best electronic brands, Taiwan brand PLC more.team of engineers and technicians have the experience ensure that each step the ideal solution.Xinqinfeng has good reputation customers,industrial furnaces,90% of our customers from overseas.
Xinqinfeng Specialized in auto spray paint machine, full-auto spraying drying line,Industrial oven, UV Curing furnace, PVD Coating machine, Robot spraying paint line twenty years.machine has industrial furnacesmany countries,such as European,North America, South America,Middle East, West African other nations. Many of the machines have CE Certification.
Xinqinfeng Factory has highly skilled engineers technicians with 20 years knowledge in powder coating liquid coating. have full ranges of industrial furnacesall types of items, from wooden to glass, cosmetic bottles more. For water-based paints like paints, vanish, UV paints, etc.
Xinqinfeng specialized in AUTO Coating machine more than 20 years. We can offered the Non-customized service,one stop coating service from cleaning,spraying,drying,metallic coating,powder coating etc.From production industrial furnaces,paint,paint teacher,air compressor ,can Provide key services make customers more worry free achieve rapid mass production.